5 Facts About Microsoft Windows
- The original Windows operating system was designed to replace MS-DOS, but technically ran on top of it.
- Microsoft Windows offered a graphical user interface for personal computer users to click on boxes rather than enter commands.
- Windows 1.0 only used 1 MB of space and 256 KB of RAM.
- The default Windows XP wallpaper, known as Bliss, was taken by Charles O’Rear in California and is considered one of the most viewed images in the world.
- There are a total of 11 versions of Windows. The latest features improved security systems, Android app availability, and more.

What Is Microsoft Windows?: Explained
On November 10, 1983, at the Plaza Hotel in New York City, happened a modest event, which will have a very important impact on the software industry in the next decades—the little known company Microsoft Corporation formally announced a graphical user interface (GUI) for its own operating system (MS-DOS), which had shipped for IBM PC and compatible computers since 1981.
Initially, the new product was developed under the name Interface Manager, but before the official introduction in 1985, the marketing gurus convinced Bill Gates that Windows is a more suitable name.
The main partner of Microsoft since 1981 was IBM when MS-DOS became the highly successful operating system that came bundled with an IBM computer. That’s why in that same November of 1983, the owner of Microsoft Bill Gates decided to show a beta version of Windows to IBM’s management. Their response was negative though, probably because IBM was working on their own operating system, called Top View
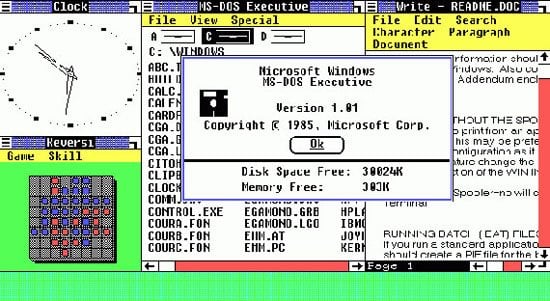
Windows 1.0 screen
©History-Computer.com
IBM Top View was released in February of 1985 as a DOS-based multitasking program manager without any GUI features. IBM promised that future versions of Top View would have a GUI. That promise was never kept, and the program was discontinued barely two years later.
It seems Bill Gates realized how profitable a successful GUI for IBM computers would be, while he had seen Apple’s Lisa computer and later the more successful Macintosh computer. Both Apple computers came with a stunning graphical user interface.
Microsoft Windows now powers approximately 90% of personal computers. Despite the mixed reviews throughout its version history and its unusual timeline of version names, Windows remains a popular operating system with many unique and convenient features.
How to Use Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows has a long version history that started in 1985. From Windows 1.0 to Windows 11, this operating system has introduced more features and streamlined capabilities. Use this basic tutorial to navigate Windows 11, the newest version of this operating system:
- Purchase a PC with Windows 11 preloaded or check for compatibility with your current personal computer.
- Press the Windows logo key + Z or hover over the window’s maximize button to open and organize Windows apps.
- Easily sync your files in OneDrive cloud storage to back up your files.
- Use the Windows logo key + S to search for files, people, email addresses, shared sites, or the web.
- Chat or video call with Microsoft Teams, which is built-in to Windows 11. Search for a Microsoft Teams tutorial for more information.
These tutorial steps help you easily navigate the latest version of this operating system. Older versions of Microsoft Windows may not have the same features or easy access to your apps, files, or Microsoft Teams.
How To Learn Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows 11, the latest version of the operating system, is designed to be easy to navigate and access for anyone used to a recent version of Windows. This version was released on October 5, 2021.
One convenient way to learn Windows is to use the Windows Tips and Tricks guide to learn directly from Microsoft. This guide offers convenient tricks and helpful tutorials on all the latest version features.
You can also take an online training course, like Windows 11: From Beginner to Advanced from Udemy. The latest books on Amazon, like the 2021 Complete User Guide to Learn Microsoft Windows 10, don’t yet cover Windows 11 but check back frequently for updated guides on the latest version of this operating system for your personal computer.
The Difference Between Microsoft Windows vs. Mac OS
While Microsoft Windows remains the most popular operating system for personal computer users around the world, this MS-DOS replacement has been competing with Mac OS from the beginning. Review the features of these two operating systems to learn more about their pros and cons.
Mac OS has been a competitor since Apple Inc. first launched it in 2001. This operating system is specifically designed for Mac computers and offers similar workstation, personal computing, and embedding functionality.
Microsoft Windows offers the following benefits compared with Mac OS:
- More convenient login options
- Expanded hardware options from Microsoft and other companies
- Improved touch capabilities and stylus support
- More streamlined voice support
There are, however, a few ways in which Microsoft Windows is at a disadvantage compared to Mac OS:
- Fewer apps
- Less mobile connectivity
There are many other ways in which the two operating systems are similar. Search, navigation, installation, and other features are largely the same between the two systems. Despite the fact that the majority of personal computers use the Windows operating system, both are competitive options.
Microsoft Windows Release History
Review the version history timeline of Microsoft Windows, from the MS-DOS graphical user interface replacement to the latest version of this dynamic operating system. While originally announced in 1983, Microsoft needed more than 2 years to launch the announced product—Microsoft Windows 1.0, which was introduced on November 20, 1985, and was initially sold for $99.
MS Windows version 1.0 was considered buggy, crude, and slow. Its rough start was made worse by a threatened lawsuit from Apple Co. In September 1985, Apple lawyers warned Bill Gates that Windows infringed on Apple copyrights and patents and that his corporation had stolen Apple’s trade secrets. Windows had similar drop-down menus, tiled windows, and mouse support as Apple’s operating system. Gates decided to make an offer to license features of Apple’s OS. Apple agreed and a contract was drawn up. A couple of years later Bill Gates had more copyright infringement problems with Apple (Apple vs. Microsoft & Hewlett-Packard copyright suit), and then he decided to claim that Apple had taken ideas from the graphical user interface developed by Xerox for Alto and Star computers.
Windows 2.0, 1987
Microsoft Windows 2.0 initially sold for $100. It was a much-improved Windows that made Windows-based computers look more like a Macintosh, introducing icons to represent programs and files, improved support for expanded-memory hardware and windows that could overlap.
Windows 3.0, 1990
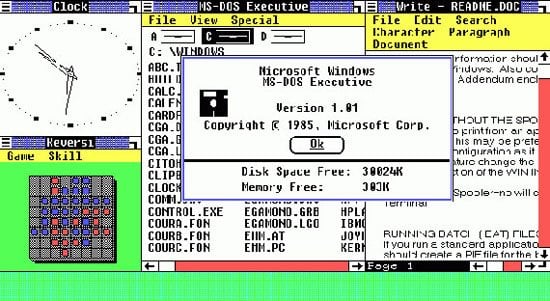
Windows 3.0 screen
©History-Computer.com
The full version was priced at $149.95 and the upgrade version at $79.95. Windows 3.0 had an improved program manager and icon system, a new file manager, support for sixteen colors, improved speed and reliability, and widespread third-party support. Programmers started writing Windows-compatible software, giving end users a reason to buy Windows 3.0. Three million copies were sold the first year.
Windows 3.1, 1992
Windows 3.1 became a smash hit, selling almost 3 million copies within the first two months of its release. It featured the new TrueType scalable font support, along with multimedia capability, object linking and embedding (OLE), application reboot capability, and more. Windows 3.x became the number one operating system installed in PCs until 1997 when Windows 95 took over.
Windows NT 3.1, 1993
Windows NT 3.1 was the first version of Windows to utilize 32-bit “flat” virtual memory addressing on 32-bit processors. Its companion product, Windows 3.1, used segmented addressing and switches from 16-bit to 32-bit addressing in pages. Windows NT was originally designed to be a powerful high-level-language-based, processor-independent, multiprocessing, multiuser operating system with features comparable to Unix. It was intended to complement consumer versions of Windows that were based on MS-DOS. NT was the first fully 32-bit version of Windows, whereas its consumer-oriented counterparts, Windows 3.1x and Windows 9x, were 16-bit/32-bit hybrids.
Windows 95, 1995
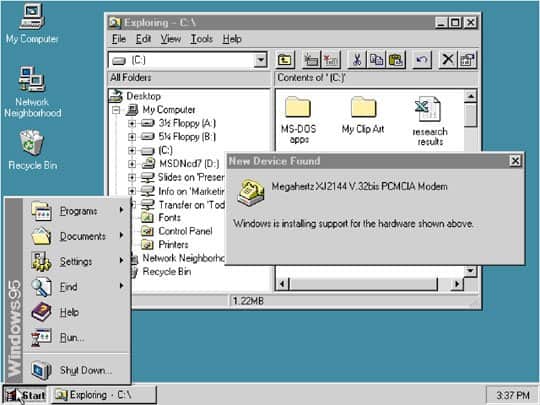
Windows 95 screen
©History-Computer.com
Thanks in part to a massive marketing campaign, Windows 95 was introduced with plenty of fanfare and rave reviews. The Start menu, internet support, and plug-and-play functionality were just a few reasons this operating system sold 7 million copies in just five weeks.
Windows 98, 1998
Windows 98 was a reliable update that performed reasonably well. It didn’t add much to the Windows 95 operating system, but it introduced a few upgrades and continued to lead the way in operating systems.
Windows 2000, 2000
Windows 2000 was just as accepted and ultimately forgettable an update as Windows 98. While not taking away from the popularity of Windows 95, it didn’t add any features or technology that ultimately changed the way users interact with the operating system.
Windows Me, 2000
Known more for its bugs, glitches, and security risks than its new functions, Windows Me was generally considered a flop. Windows Me is still considered one of the worst operating systems to ever have been created. This reflects issues with the system, but also the sense of letdown when comparing Windows Me with Windows 95 and other popular versions.
Windows XP, 2001
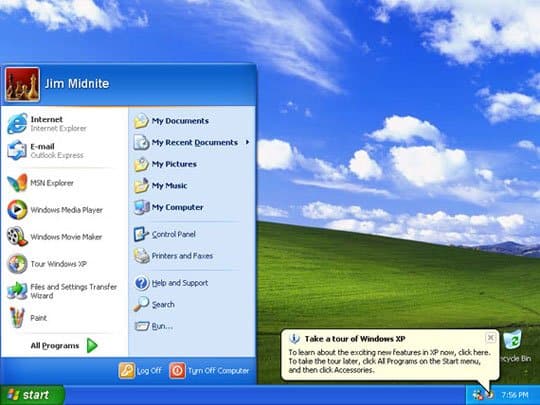
Windows XP screen
©History-Computer.com
After the less-than-memorable versions, Windows XP was introduced as a major improvement. It remains an extremely popular operating system, despite losing mainstream support in 2009. Windows XP introduced a stylish interface, convenient taskbar, and updated infrastructure.
Windows Vista, 2007
The next desktop OS of Microsoft was released more than five years after the introduction of its predecessor, the longest time span between successive releases of Windows desktop operating systems. Windows Vista (known by its code name “Longhorn”) was released in January 2007. It contains many changes and new features, including an updated graphical user interface and visual style dubbed Aero, a redesigned search function, multimedia tools including Windows DVD Maker, and redesigned networking, audio, print, and display subsystems. Vista aims to increase the level of communication between machines on a home network, using peer-to-peer technology to simplify sharing files and media between computers and devices. Windows Vista includes version 3.0 of the .NET Framework, allowing software developers to write applications without traditional Windows APIs.
Commonly known as the second-worst operating system in history, just after Windows Me, Windows Vista failed to live up to expectations. Not only was it seen as a letdown compared to Windows XP, but it didn’t have enough hardware drivers to support many monitors or printers. Clunky features and poor infrastructural decisions caused my users to switch back to XP.
Windows 7, 2009
The welcomed relief users wanted after Vista, Windows 7 lived up to the quality of operating systems Windows has been famous for. It came with handwriting recognition, DirectAccess, an updated Windows Media Center, and plenty of other features to help users forget all about the poor design of Vista.
Unlike its predecessor, which introduced a large number of new features, Windows 7 was intended to be a more focused, incremental upgrade to the Windows line, with the goal of being compatible with applications and hardware with which Windows Vista is already compatible. It focused on multi-touch support, a redesigned Windows Shell with a new taskbar, referred to as the Superbar, a home networking system called HomeGroup, and performance improvements. Some standard applications that have been included with prior releases of Microsoft Windows, including Windows Calendar, Windows Mail, Windows Movie Maker, and Windows Photo Gallery, are not included in Windows 7, most are instead offered separately at no charge as part of the Windows Live Essentials suite.
Windows 8, 2012
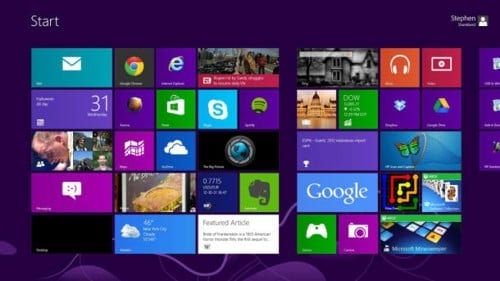
Windows 8 screen
©History-Computer.com
Microsoft Windows needed to compete in a new market; hybrid OS. Max offered dynamic synergy between tablets, phones, and laptops, so Windows 8 was the first attempt of Windows to get in on the game. The lack of a Start menu and the dramatic visual changes weren’t received well, making Windows 8 yet another letdown in the version history of Windows.
The desktop was changed radically to make way for the new so-called Modern UI (User Interface). There was no more Start button, as this interface was designed to be used with touchscreens as well as with a mouse and keyboard, and requires programs to be written specially for it. These programs will be downloaded via the new Windows Store, or from developers’ websites.
Microsoft claims that Windows 8 has significant security improvements, better battery life, and faster boot time. Windows 8 features the new “Hybrid Boot” mode (which hibernates the Windows kernel on shutdown to speed up the next bootup).
Task Manager has also been redesigned, including a new processes tab with the option to display fewer or more details of running applications and background processes, a heat map using different colors indicating the level of resource usage, etc.
Windows 10, 2015
Declared the last Windows version when it was first released, Microsoft 10 brought back the Start menu and introduced a number of other features. This declaration is the official reason why Microsoft skipped Windows 9, but this announcement still left a number of users confused. This operating system underwent a number of version updates before being replaced by Windows 11.
Windows 11, 2021
Windows 11 offers the most up-to-date version of Windows 11. Most critics have praised its sleek design and easy navigation. Its improved security systems, Android app availability, and other features help it compete with the latest Mac OS and outperform Windows 10.