Key Points:
- Since the 1970’s, Cray has been a leading supercomputer company, and is now a subsidiary of Hewlett Packard Enterprise.
- Today, Cray research focuses on revolutionary designs and innovations in supercomputing by working with big data in global scientific and industrial organizations.
- Cray’s first commercial customer was Ford Motor Company, which purchased a Cray C90 in 1991, leading them to seek more commercial opportunities.
The History of Cray: What to Know
From the world’s fastest computer in the 1970s to modern exascale computing, Cray has been a leading supercomputer company since the start of the field. Cray is now a subsidiary of Hewlett Packard Enterprise but its history started with Seymour Cray founding Cray Research.

The initial years of Cray Research focused on creating the fastest scientific computing systems. The company still focuses on revolutionary designs and innovations in supercomputing, by working with big data in global scientific and industrial organizations.
The Founding of Cray: How It Happened
It all started with one man’s goal to create the fastest computer. Seymour Cray started his journey to founding his company in 1950. He joined Engineering Research Associates, or ERA, and helped design the ERA 1103. This is known as the first commercially successful scientific computer.
After working with ERA, Seymour Cray joined the Control Data Corporation, or CDC, in 1958. He worked with CDC to create an improved version of the ERA 1103 and eventually developed the CDC 6600 in 1964. The programming language Pascal was created on CDC 6000 series computers and it had other renowned specs, including data storage and processing power.
After these successes, Cray formed his own company in 1950 to work on Cray-1. It was then the fastest supercomputer, with the first three models being sold to Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Los Alamos National Laboratory, and the National Center for Atmospheric Research.

Cray Through the Decades
1970s and 1980s – The World’s Fastest Computers
Seymour Cray never expected the Cray-1 to be so commercially successful. He set the price to sell only a dozen machines but ended up selling over 80. The Cray-2 then became the first to reach over 1 gigaflop. The early years of Cray Research made history and saw the following supercomputers designed with industry-leading specs:
- Cray-1: 1976
- Cray X-MP: 1982
- Cray-2: 1985
- Cray Y-MP: 1988
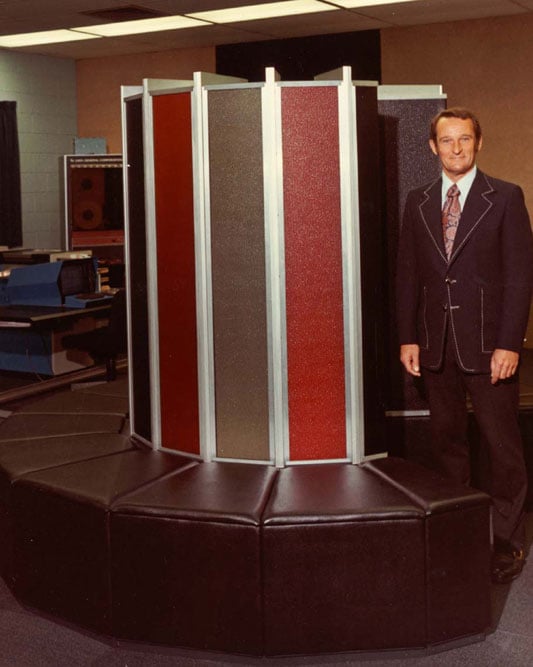

1990s and 2000s – Commercial Opportunities
The first commercial customer, Ford Motor Company, purchased a Cray C90 in 1991. The company moved from scientific and governmental supercomputer solutions to commercial opportunities. These decades saw the first wireless supercomputer and dramatic increases in computing power with these models:
- Cray C90: 1991
- Cray Y-MP EL: 1991
- Cray M90: 1992
- Cray T3D: 1993
- Cray J90: 1994
- Cray T90: 1995
- Cray T3E: 1995
- Cray SV1 Series: 1998
- Cray X1/X1E: 2002
- Cray XT Series: 2004
- Cray XMT: 2006
2010s – Big Data Processing Power
The 2010s saw dramatic leaps in supercomputer specs. Massive processing power improvements allowed scientists, government organizations, and commercial clients to harness big data in new ways. From discovering the core is the reason Earth’s magnetic field keeps moving west to breaking the exascale barrier, these Cray supercomputers continued to make history:
- Cray XE6: 2010
- Cray XK Series: 2011
- Cray XC Series: 2012
- Cray Urika Platforms: 2012
- Cray CS Series: 2013
- Cray CS-Storm: 2014
- HPE Cray EX: 2018
What Are the Most Important Inventions From Cray?
Cray has made many major processing power leaps and innovative system designs over the decades. While many designs could make the list, these three represent some of the most important inventions from Cray.
Cray-1
The fastest supercomputer of its time, Cray-1 was the primary reason Seymour Cray is often known as the father of modern supercomputing. It could perform 160 megaflops, which broke the record during its time. It contained 60 miles of wire and, despite its price of $5 to $8 million, sold over 80 models.
Cray-2
Thanks to liquid immersion cooling and a peak speed of 1.9 gigaflops, the Cray-2 supercomputer made significant improvements over the first model in less than 10 years. Its first customer was the National Magnetic Fusion Energy Computer Center and 27 were sold in total.
HPE Cray EX
Thanks to Slingshot™ interconnection and AI workloads, the HPE Cray EX series offered three Shasta system supercomputers as the first three U.S. supercomputers capable of exascale computing. Exascale offers a significant improvement in computing technology as researchers tackle major global issues.
How Does Cray Make Money?
Cray designs and manufactures supercomputers for sale to scientific and commercial clients. It also manufactures data storage and analytics systems. The company has continued to compete to create the fastest, most efficient supercomputers in the world since its founding in 1972 and since being acquired by Hewlett Packard.
Up Next:
- Atlas Computer Explained – Everything You Need To Know Learn about this early experimental computer which was a precursor in the evolution of super-computers.
- Shakey the Robot Explained: Everything You Need to Know Shakey the Robot was the first of its kind to have a perception of its environment. Find out more in this fascinating article.
- Meet Charles Babbage – Complete Biography Discover the biography of Charles Babbage–mechanical engineer, mathematician, philosopher, and inventor.